 When it comes to choosing the right hardware for your business, there are a lot of pros and cons to consider.
When it comes to choosing the right hardware for your business, there are a lot of pros and cons to consider.
Should you continue using traditional laptops or desktops or would your organization benefit from transitioning to thin clients?
What is a Thin Client?
Unlike a traditional computer that relies on its localized hard drive, a thin client operates off resources stored on a centralized server. Thin clients access sensitive data, applications, and memory by connecting to the remote server environment.
Why are Thin Clients Beneficial?
 Most businesses appreciate the cost savings associated with thin clients. Because they rely on server-side centralization, thin clients save companies on licensing costs.
Most businesses appreciate the cost savings associated with thin clients. Because they rely on server-side centralization, thin clients save companies on licensing costs.
The realities of the modern business environment gives rise to concerns other than cost, however. With cybercrime on the rise the security of your sensitive client information and other pieces of critical data is paramount.
Even small businesses need to be aware of the threat from cybercriminals. Making the right equipment choices can play a key role in your overall security posture.
Because a thin client is server-restricted, it can’t run unauthorized software and data isn’t stored natively on the device. Everything is controlled at the server making monitoring and management much easier.
 Thin clients also make better use of and make better use of IT support and resources. All upgrades and security patches are performed at the server level rather than on each endpoint machine. By reducing the potential for downtime, thin clients tend to increase productivity for end users and IT professionals alike.
Thin clients also make better use of and make better use of IT support and resources. All upgrades and security patches are performed at the server level rather than on each endpoint machine. By reducing the potential for downtime, thin clients tend to increase productivity for end users and IT professionals alike.
And finally, thin clients allow for easy scaling using virtual desktops. The thin client architecture gives employees flexibility by giving users the option to bring their own device when your company policy supports that initiative. Your server also allows you to bring on temporary workers and makes it easier to onboard them and get them up to speed and working efficiently faster.
How are Thin Clients Typically Used?
Since thin clients are slimmed down devices, they are best suited for shared terminal services, browser-based computing or desktop virtualization.
As a shared terminal, the end user activity is limited by use of the same operating system and applications. Most of the activity will require prior IT approval which can be beneficial to organizations. The shared terminal set up allows for specific, safe, or properly protected applications to be accessed on the thin client.
Thin clients can also be used for browser-based applications. Rather than using a centralized server, the application is accessed through the internet and the functions using the client’s browser. In this scenario, the data processing occurs on the machine itself, but the data and software are accessed via a network connection.
In a desktop virtualization (VDI) scenario, each individual desktop exists within a virtual machine, which is a partition inside the centralized server or a cloud hosting partner’s secure data center.
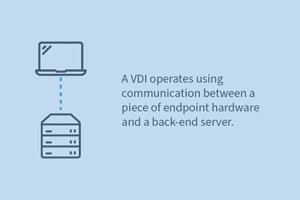 A VDI operates using communication between a piece of endpoint hardware and a back-end server. The thin client makes a request to the server. The server fulfills the request via a network connection, usually the internet.
A VDI operates using communication between a piece of endpoint hardware and a back-end server. The thin client makes a request to the server. The server fulfills the request via a network connection, usually the internet.
Depending on the right use case for thin clients in your organization, you may be able to modify existing PC’s into thin clients.
Why We Ask About Thin Clients During the Discovery Process
At CyberlinkASP, we know how important it is to be familiar with our clients’ current technology infrastructure so we can have productive conversations about your needs and goals.
We want to ask the right questions at every stage of our relationship with you so we can provide optimized performance that meets the business objectives for your company.
Our team of highly trained, industry experts are ready to help you increase your productivity while reducing overall costs. Schedule your call today.

